Table of contents:
- Understanding Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
- Types of AGVs
- AGV navigation and control technologies
- Safety standards and features
- Applications of AGVs across industries
- Benefits of implementing AGVs
- Future of AGVs
- Choosing the right AGV solution
- Conclusion
- Additional resources
- AGV questions and answers
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are one of the cornerstones of dynamic industrial automation, contributing to significant improvements in operational efficiency, safety and adaptability in a wide range of industries.
At Solving, we specialize in delivering AGV solutions tailored to meet the diverse needs of our clients, such as manufacturing plants and warehouses.
Our goal with this comprehensive article is not just to inform but also to highlight the enormous potential and versatility of AGVs to an audience ranging from industry veterans to curious beginners.
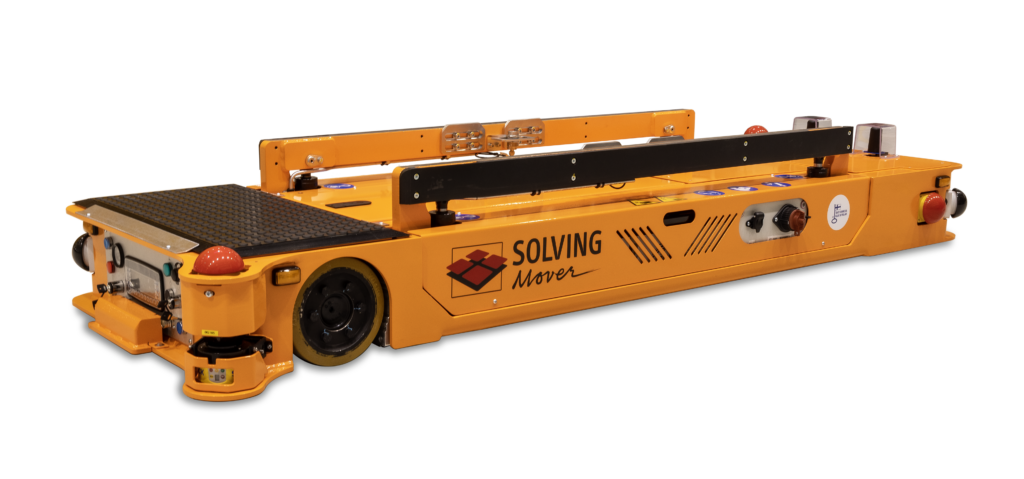
AGVs are sophisticated, autonomous vehicles designed to transport materials and goods within industrial environments without direct human oversight. They follow thoroughly predefined paths, using a variety of navigation technologies, such as magnetic and laser, to navigate complex environments with precision and reliability.
Originating in the mid-20th century, the application and capabilities of AGVs have evolved in line with technological developments and have become indispensable in automating and streamlining supply chain and manufacturing processes.
Now, let’s give you an overview of AGVs, explaining the different types, the complex navigation technologies, their wide range of applications in various industries, and the great benefits they offer to modern business operations.
As Solving, our commitment goes beyond providing AGV solutions; we strive to give companies the knowledge they need to navigate the future of automation confidently.
Whether you are already deeply involved in the automation industry or have just started exploring the possibilities it offers, this guide promises to give you deep insights into the changing world of Automated Guided Vehicles.
Are you looking for AGV’s for your industry?
Learn how other companies all aroound the world has transformed their material handling with AGV’s on the product page. If you just want information about AGV’s overall, keep reading!
Understanding Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Definition of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are self-propelled robots equipped with advanced control systems, enabling them to transport materials and goods within industrial and commercial environments.
These vehicles are essential for automating logistical and manufacturing processes and are designed to operate autonomously by following predefined paths, thus enhancing efficiency, safety, and operational continuity.
Historical evolution of AGVs
The concept of AGVs dates to the 1950s, marking a significant milestone in the journey toward industrial automation. Initially conceived as tow vehicles that followed wires in the floor, AGVs have evolved in response to technological advancements and changing industrial needs.
The development of microprocessors and wireless communication in the latter half of the 20th century enabled more sophisticated control and navigation capabilities, leading to the diversity of AGVs seen today.
This evolution reflects the increasing demand for flexible, efficient, and safe material handling solutions across various sectors. Read more about the history of AGVs here.
Differences between AGVs and AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots)
While AGVs and AMRs both serve to automate material transport, they differ in navigation and operational flexibility:
- AGVs typically follow fixed routes determined by guidance systems such as magnetic sports or laser-targeted paths. This makes them highly reliable for repetitive tasks where the environment remains consistent. For large and heavy loads AGV is a better solution.
- AMRs, on the other hand, boast advanced sensors and onboard intelligence that allow them to understand and interact with their environment dynamically. This enables AMRs to navigate autonomously, plan routes in real-time, and avoid obstacles without pre-defined paths, offering greater flexibility in adapting to changes within a facility.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses considering automation solutions, as the choice between AGVs and AMRs will significantly depend on the specific operational needs, the loads to be transported, the desired level of adaptability, and the environment in which these vehicles will operate.
Types of AGVs
The versatility of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) is showcased through their varied types, each designed to fulfill specific roles within industrial, commercial, and healthcare settings. Below, we review the primary categories of AGVs, their functionalities, applications, and their unique advantages.
Automated Guided Carts (AGCs)
Basic Functionality and Applications: AGCs represent the most fundamental type of AGVs, designed for efficiency. These carts follow a predetermined path marked by magnets in the floor, magnetic tape, or a painted line, making them ideal for repetitive tasks such as transporting materials between fixed points. Common applications include assembly lines, where their straightforward operation supports consistent workflow.

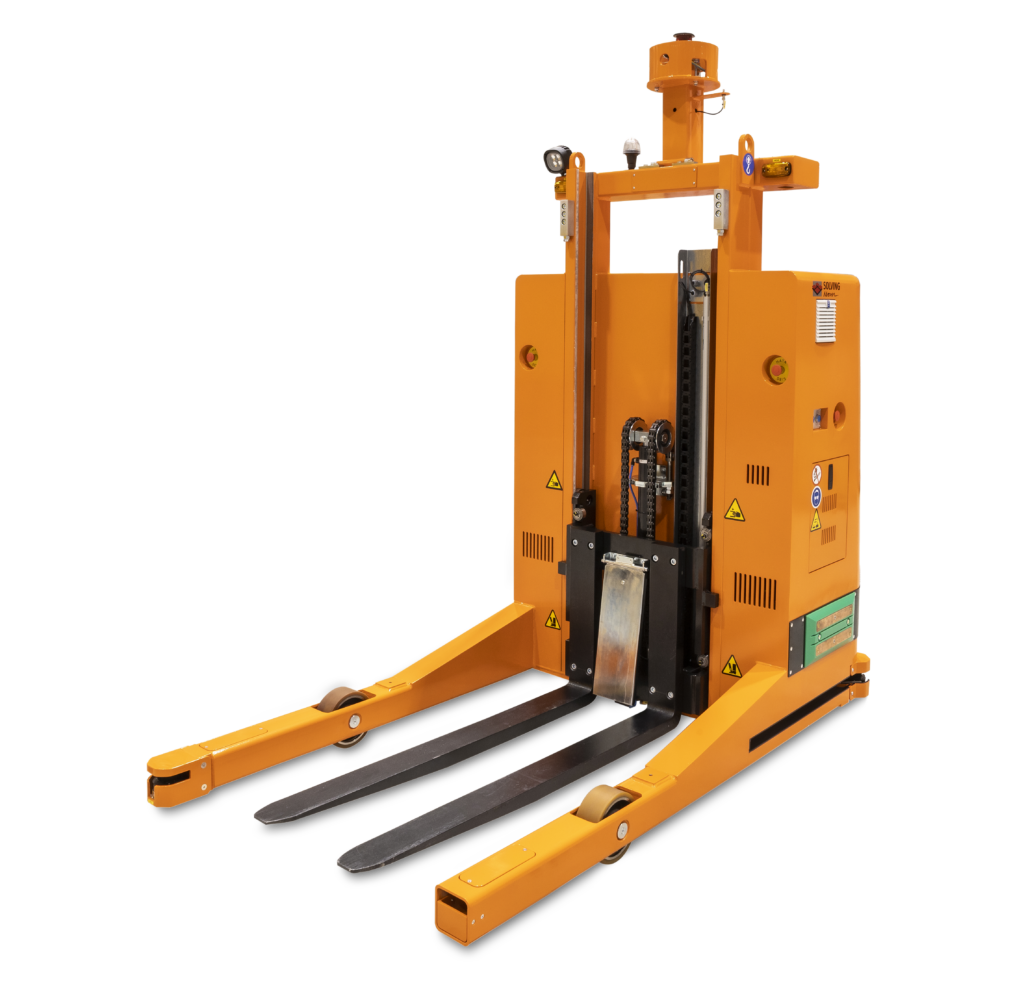
Forklift AGVs
Capabilities and Comparison with Traditional Forklifts: Forklift AGVs combine the versatility of traditional forklifts with autonomous navigation. Capable of lifting and transporting pallets, these AGVs enhance safety and reduce labor costs in warehouses and distribution centers. Unlike manual forklifts, their autonomous operation minimizes the risk of accidents and improves efficiency by operating around the clock without fatigue.

Towing AGVs
Features and Industrial Applications: Towing AGVs, or tugger AGVs, are designed to pull carts or trailers loaded with goods. They are particularly effective for moving heavy loads across large facilities, such as automotive manufacturing plants, where materials must be transported from storage areas to production lines. Their strength lies in their capacity to tow multiple loads simultaneously, streamlining the supply chain logistics.

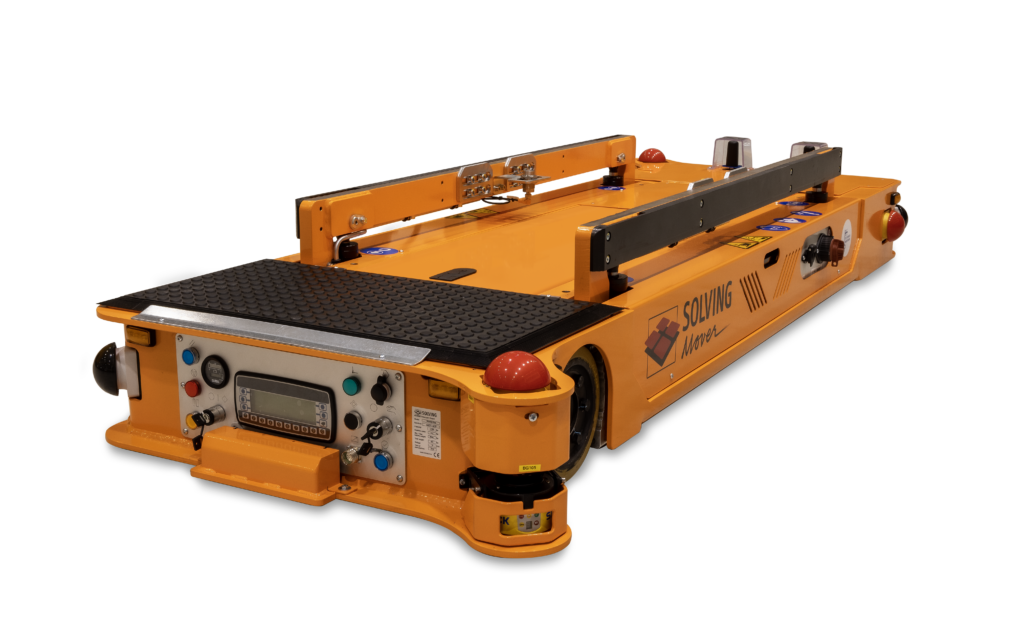
Unit load carriers
Design and Utility: Unit Load Carriers are specialized AGVs that transport single loads, such as pallets or large containers, directly on their frames. These AGVs move items from warehousing areas to production sites, optimizing load handling by eliminating the need for additional equipment for loading and unloading.
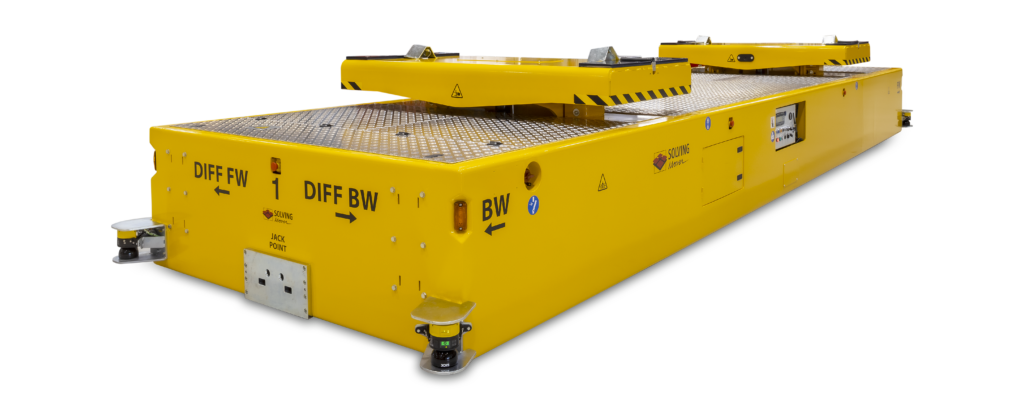

Heavy load carriers
Construction and Use Cases: Heavy Load Carriers are heavy-duty AGVs, built to transport extremely heavy or oversized loads. Their robust construction allows for applications in industries like steel manufacturing and heavy machinery, where they move large items that exceed the capacity of other vehicle types.
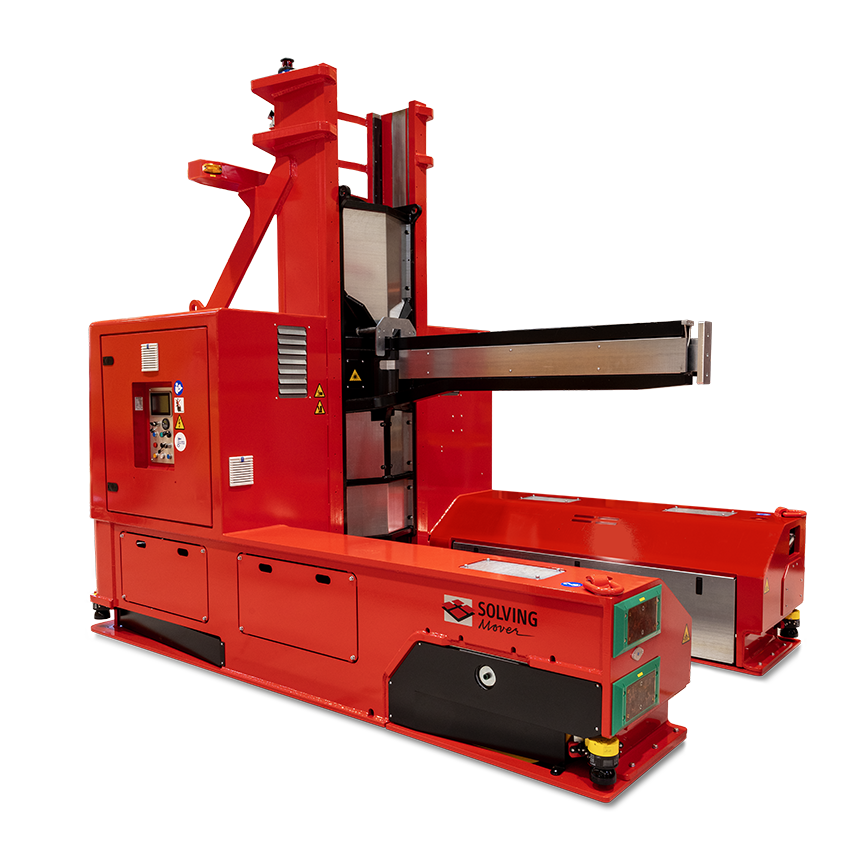

Custom AGVs
The role of customization in meeting specific industry needs: Custom AGVs are tailored solutions designed to meet unique operational challenges. Through customization, AGVs can be equipped with specific tools, lifting mechanisms, or software integrations, ensuring they perfectly suit the complex requirements of various sectors, including aerospace, specialized manufacturing, and more.
Customization is the core of Solving’s AGV solutions, emphasizing the company’s innovative approach to developing AGVs that are precisely tailored to meet unique operational challenges. From specialized manufacturing to aerospace, Solving’s custom AGVs are designed to meet the specific requirements of different industries, demonstrating the company’s versatility and customer orientation.
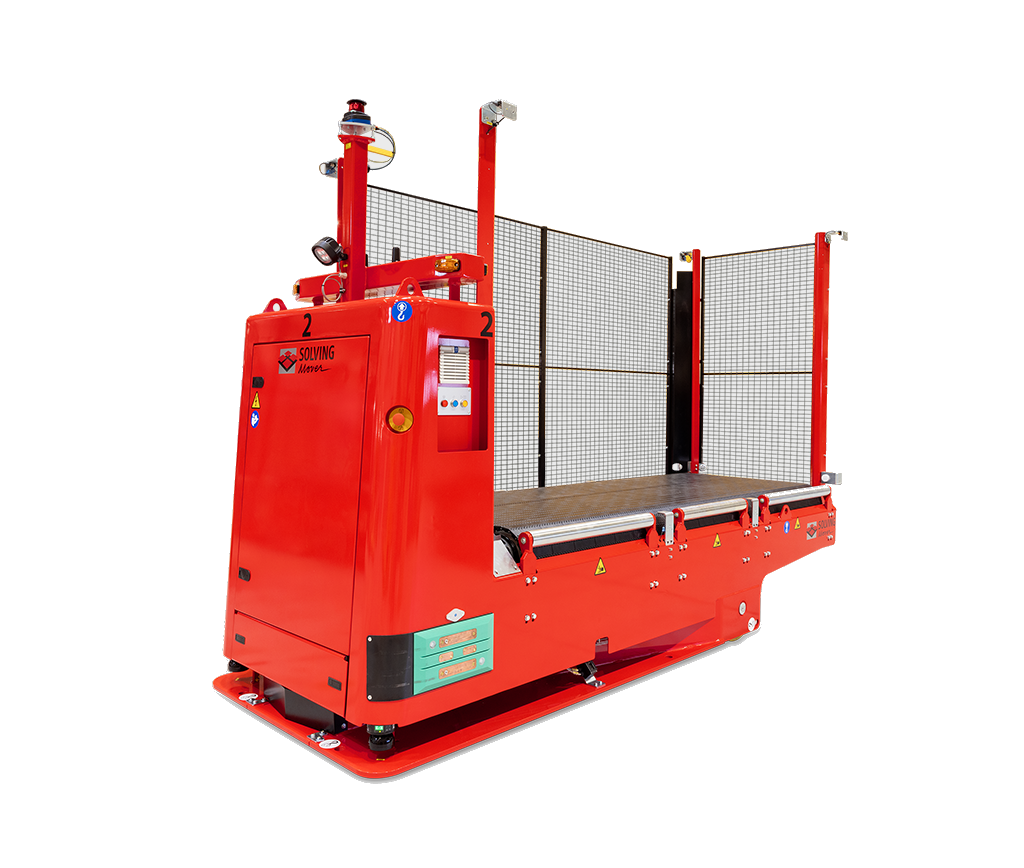

Specialized AGVs
Solving’s portfolio also includes the potential for specialized AGVs, such as those designed for unique applications beyond traditional material handling. This area allows Solving to develop AGVs for niche markets, including food and nuclear industries, and to use its expertise to meet new requirements.
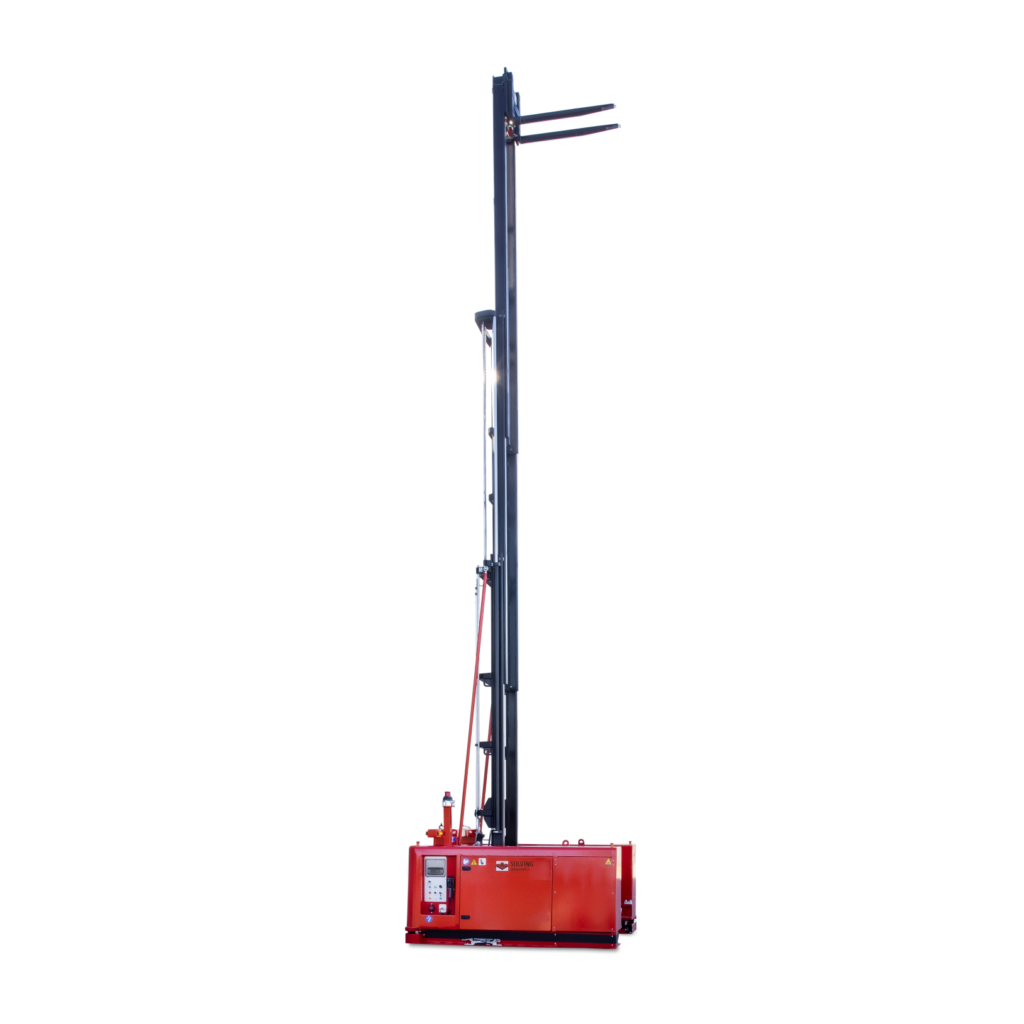

Each AGV type offers a distinct set of capabilities, thus emphasizing that AGV technology can be adapted to a broad range of industrial and non-industrial applications. As businesses strive to optimize operations and enhance efficiency, the selection of the appropriate AGV type becomes a strategic decision, critical to achieving operational excellence.

Download all AGV whitepapers
Solving Movers are customized to suit the most varying applications. Here you can download all our AGV whitepapers at once and perhaps find an AGV installation we have made that is similar to your specific requirements. If you find something of interest, contact our AGV experts for further discussions.
AGV navigation and control technologies
As the core of Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) functionality, control and navigation technologies determine an AGV’s efficiency, flexibility, and suitability for specific applications.
Solving utilizes a range of advanced technologies to ensure its AGVs can navigate complex industrial landscapes with precision. This section describes the various navigation technologies used in Solving’s AGVs, highlighting their implementation, advantages, and applications.
Magnetic guide tape
Magnetic guide tape involves laying down a magnetic or metallic tape on the facility floor, which AGVs follow using magnetic sensors. This straightforward and cost-effective method offers reliability and ease of path modification. Solving utilizes magnetic guide tape in settings where routes are fixed but may require occasional adjustments, ensuring a balance between consistency and adaptability.
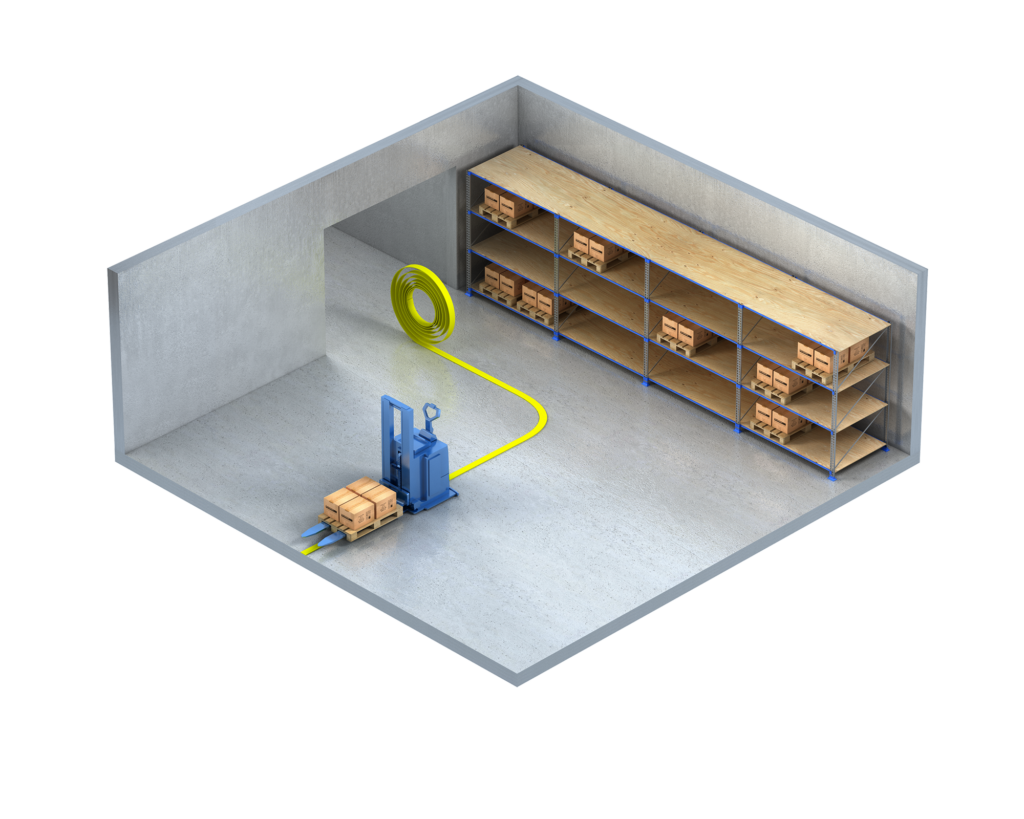
Laser navigation
Laser navigation, characterized by flexibility, uses a rotating laser scanner to detect reflectors placed in the building. This technology allows for real-time path planning and obstacle avoidance, making it ideal for dynamic environments. Solving’s laser-guided AGVs exemplify the technology’s precision and adaptability, capable of navigating complex spaces with minimal infrastructure changes.
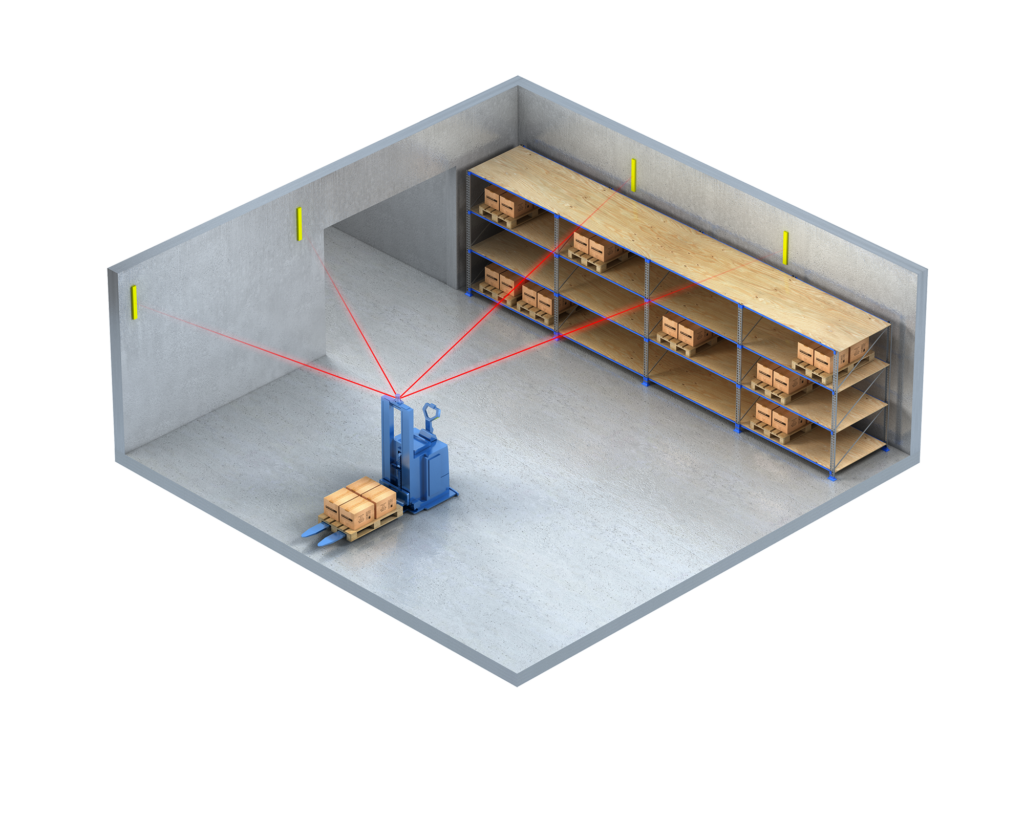
Contour navigation
Contour navigation, also known as natural feature navigation, utilizes the AGV’s onboard cameras and sensors to identify and follow the contours of the facility’s natural landscape. This method does not require any physical modifications to the environment, making it highly adaptable and minimally invasive. Solving employs contour navigation in settings where the layout remains relatively stable over time.
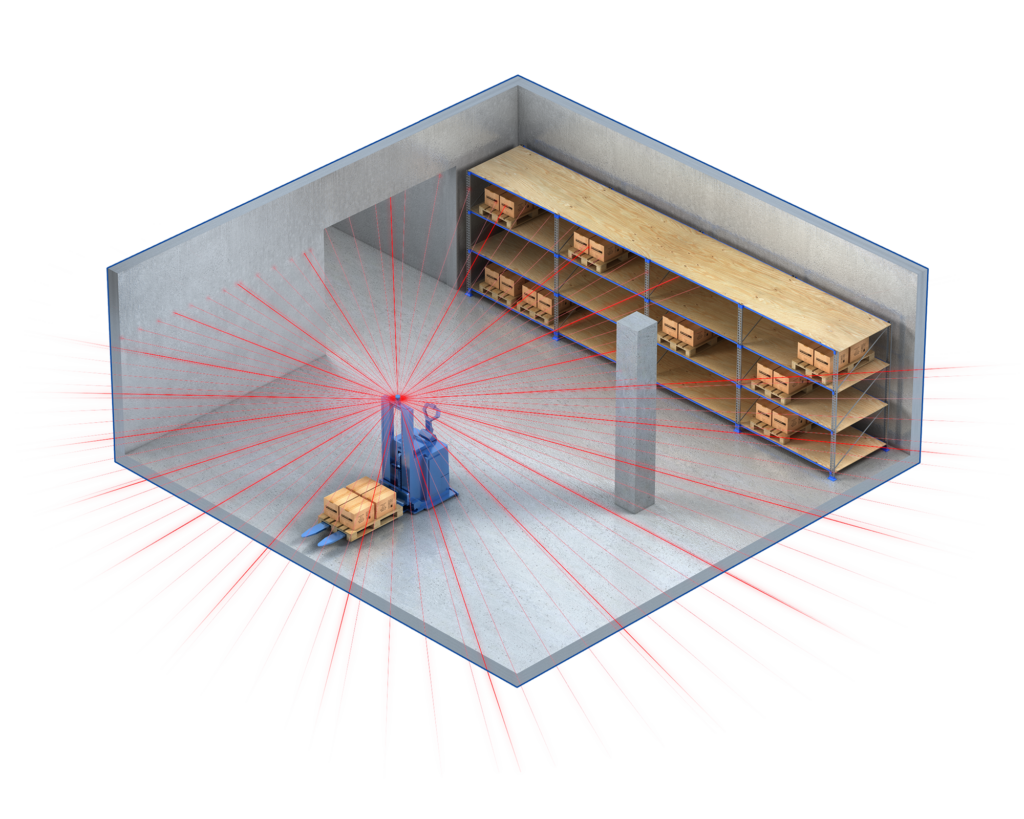
Magnetic spot navigation
Magnetic spot navigation involves embedding small, discrete magnetic markers in the facility’s floor at specific intervals. AGVs equipped with magnetic sensors detect these markers to determine their path and make precise navigational decisions. Solving integrates magnetic spot navigation in applications requiring a durable navigation system and can also be used as a complement to laser or contour navigation.
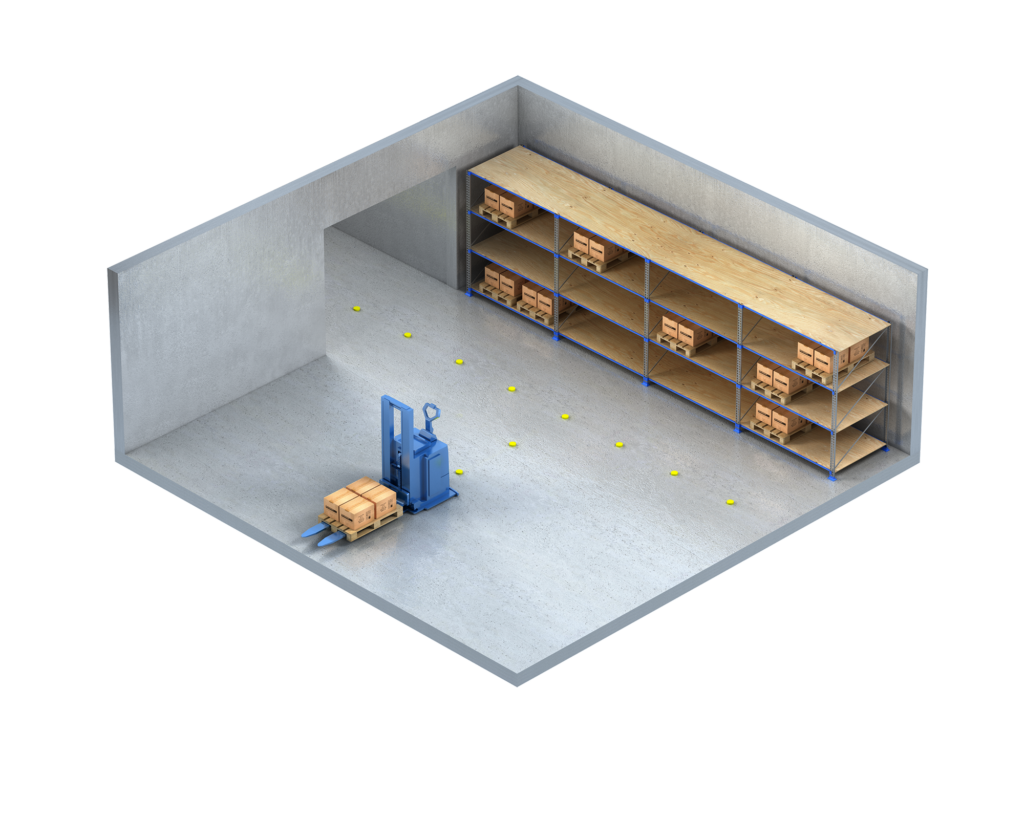

Barcode navigation
Barcode navigation uses barcodes placed at intervals along the AGV’s route and is a cutting-edge approach for defined pathways. The AGV scans these barcodes to determine its location and navigate the predetermined path. This method is cost-effective and allows for relatively simple route modifications. Barcode navigation is used in straightforward applications where high navigation accuracy is required without significant infrastructure modifications.
Multi-navigation
Multi-navigation is an integration for enhanced flexibility and precision because it combines two or more navigation technologies to utilize their individual strengths and mitigate their weaknesses. This approach allows Solving’s AGVs to operate in complex environments with varying requirements, such as facilities that combine open spaces with tightly structured aisles. By using multi-navigation, Solving ensures its AGVs can adapt to diverse operational contexts, providing customers with solutions that are both versatile and reliable.
Comparison of navigation technologies
Advantages, disadvantages, and suitability: Each navigation technology comes with its set of strengths and limitations.
Solving’s expertise in integrating these technologies ensures that each AGV solution is optimized for its intended application, whether that involves navigating tight warehouse aisles, adapting to changing manufacturing layouts, or operating in environments where traditional navigation aids are impractical. By using the appropriate navigation technology, Solving ensures that its AGVs deliver superior performance, safety, and efficiency.
Safety standards and features
The integration of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) into industrial operations requires strict attention to safety standards and the incorporation of essential safety features. These measures ensure the well-being of personnel and the protection of goods and infrastructure in the working environment.
This section describes the main safety standards for AGVs, the critical safety features they are equipped with, and the overall importance of safety in AGV design and operation.
Overview of safety standards
Several international and regional standards provide the framework for AGV safety, ensuring consistency and reliability across the industry:
- ANSI/ITSDF B56.5 (United States): This standard outlines the safety requirements for the design, operation, and maintenance of AGVs. It addresses aspects such as emergency stopping, audible and visible warning devices, and AGV navigation and stability.
- EN ISO 3691-4 (Europe): Part of the ISO 3691 series on industrial trucks, this standard specifies safety requirements and verification for driverless industrial trucks and their systems. It covers the integration of AGVs into workplaces, focusing on the interaction between AGVs and humans.
- R15.08 (United States): A relatively new standard by the Robotic Industries Association (RIA), focusing on industrial mobile robots, including AGVs. It complements existing standards by addressing the unique challenges posed by more autonomous mobile robotics.
These standards ensure that AGVs are designed, operated, and maintained with safety as a paramount concern, protecting both human operators and the automated systems themselves.
Essential safety features of AGVs
To comply with these safety standards, AGVs are equipped with a range of safety features designed to prevent accidents and ensure the smooth integration of these vehicles into human-centric work environments:
- Laser scanners: Mounted on AGVs, laser scanners continuously scan the vehicle’s surroundings to detect obstacles, adjusting the AGV’s path or stopping it entirely to avoid collisions.
- Bumpers: Pressure-sensitive bumpers provide an additional layer of safety, bringing the AGV to an immediate halt upon contact with an object or person.
- Emergency stops (E-stops): E-stop buttons are a critical safety feature allowing human operators to immediately stop an AGV in case of an emergency, ensuring quick response to potential hazards.
- Audible and visible warning devices: To enhance awareness among nearby workers, AGVs are often equipped with alarms, lights, or other signals indicating their operational status and movements.
The importance of safety in AGV design and operation
Safety is an integral part of the design and operation of AGVs and guides the development of technologies and operational protocols that protect human workers while enhancing efficiency. A safe AGV system promotes a harmonious working relationship between humans and machines, facilitates the adoption of automation technologies and supports the creation of more productive and safe industrial environments. By strictly adhering to safety standards and implementing comprehensive safety features, the industry can ensure that AGVs contribute positively to the modern workplace, maximizing both protection and performance.
Applications of AGVs across industries
The versatility and adaptability of Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have made them a valuable resource in a wide range of industries. By automating material handling and logistics, AGVs improve efficiency, safety, and productivity, and have proven to be a game-changer in various sectors. Solving AGVs have been installed in various industries, ranging from aerospace and vehicle manufacturing to food and steel industry and many other industries. Here, we explore their key roles and unique applications in different industries, including a groundbreaking project in the nuclear sector.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, AGVs streamline assembly lines and production processes by ensuring a steady and reliable supply of materials and components. They reduce manual handling, minimize production delays, and improve workplace safety, making them an essential part of modern manufacturing operations.
Warehousing and distribution
AGVs transform warehousing and distribution centers by optimizing storage capabilities and improving operational efficiency. They automate tasks such as pallet moving, order picking, and inventory management, allowing for faster response times and reduced labor costs.
Healthcare
In healthcare facilities, AGVs play a crucial role in logistics and patient care by automating the transport of surgical instruments, medicines, specimens, linens, and meals. This automation supports infection control measures, reduces manual labor, and allows healthcare professionals to focus more on patient care.
Food and beverage
The food and beverage industry benefits from AGVs by streamlining processes from production to packaging. AGVs ensure the timely and safe transport of raw materials, finished products, and critical supplies, maintaining hygiene standards and enhancing production line efficiency.
Automotive
AGVs support the automotive industry by automating assembly and supply chain operations. They transport parts, assemblies, and finished vehicles throughout manufacturing facilities, reducing production time and increasing throughput.
Nuclear
Solving’s involvement with Posiva’s ONKALO® Repository showcases the specialized application of AGVs in the nuclear sector. The project involves the use of customized Solving Movers for the safe transport of disposal canisters with spent nuclear fuel. These AGVs are equipped with optical laser scanners for navigation and are designed to operate under strict safety protocols, highlighting the potential of AGVs to contribute to environmentally sensitive and highly regulated industries.
Specialized applications
AGVs find specialized applications in industries like pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and more, where precision, safety, and efficiency are crucial. They are customized to meet specific operational needs, such as handling sensitive materials, operating in cleanroom environments, or navigating complex industrial environments.
Integration of AGVs in these diverse industries ensures scalable, efficient, and safe solutions for material handling and logistics challenges. The case of Solving’s AGV system for Posiva’s ONKALO® Repository particularly illustrates the innovative use of AGV technology to manage complex and critical tasks, setting a precedent for future applications in the nuclear sector and beyond. As industries continue to evolve and seek more sustainable and efficient operations, AGVs will play an even more important role in achieving these goals.
Benefits of implementing AGVs
The implementation of AGVs in various industries brings a variety of benefits, from operational improvements to financial savings and environmental benefits.
Efficiency and productivity
AGVs significantly optimize operations by automating the transport of materials, reducing the time and effort required for manual handling. Their precision and reliability ensure a smooth flow of goods, minimizing delays and increasing overall productivity.
Safety
Implementing AGVs reduces workplace accidents by taking over tasks that are hazardous for humans, such as transporting heavy loads or handling dangerous materials. Equipped with advanced safety features, AGVs ensure safe operation in facilities, protecting both workers and equipment.
Cost-effectiveness
While the initial investment in AGVs may be substantial, the long-term financial benefits include reduced labor costs, lower accident-related expenses, and minimized product damage. AGVs offer a high return on investment through continuous, efficient operations and the ability to operate 24/7 without fatigue.
Flexibility and scalability
AGVs are designed to meet customer requirements. Their routes and tasks can be reconfigured as operational requirements change, and additional units can be integrated into existing systems to scale operations.
Environmental impact
AGVs contribute to sustainability efforts by optimizing energy use and reducing waste. Electrically powered AGVs emit no pollutants, supporting initiatives to create greener, more sustainable facilities. Solving’s durable AGVs are built to last in tough industrial environments. As they are battery-powered they do not pollute and, being custom-made, only the components required for a particular Mover are procured – no more, no less, no excess.
Implementing AGVs is a strategic decision that enables industries to face the challenges of modern logistics and manufacturing, offering a competitive edge through improved efficiency, safety, and adaptability.
Future of AGVs
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are facing a revolutionary change, driven by rapid technological advancements and the integration of artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). As AGVs become increasingly sophisticated, their role in industrial operations will expand, presenting both challenges and opportunities for the next generation of AGVs.
Technological advancements on the horizon
The future of AGVs is characterized by the development of more advanced navigation and control systems, enhanced safety features, and greater operational flexibility. Innovations in battery technology and energy efficiency are expected to extend the operational life of AGVs, while improvements in sensor technology will increase their ability to interact with their environment, making them even safer and more reliable.
The growing role of AI and machine learning in AGV operations
AI and machine learning are at the forefront of the next wave of AGV development, enabling these vehicles to make intelligent decisions in real-time. Through AI, AGVs can optimize their routes, predict maintenance needs, and adapt to changes in their environment with minimal human intervention. Machine learning algorithms allow AGVs to improve their performance over time, learning from past operations to increase efficiency and safety.
Integration with the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and smart factories
The integration of AGVs with IIoT and smart factory ecosystems represents a significant shift towards fully automated and interconnected industrial environments. AGVs will communicate not only with each other but also with other machinery and systems within the facility, allowing them to control complex operations with precision.
Challenges and opportunities for the next generation of AGVs
As AGVs continue to advance, they face challenges such as the need for standardization in different technologies and platforms, ensuring cybersecurity within increasingly connected environments, and overcoming technical and infrastructural barriers to adoption. But these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth in the AGV sector.
In the future, AGVs will likely become more autonomous, capable of handling a wider range of tasks, and integrated into more aspects of industrial and commercial operations. Opportunities to customize AGV solutions will increase to meet specific industry needs and offer solutions to previously unexplored challenges.
The increasing sophistication of AGVs, combined with the broader adoption of smart manufacturing principles, makes AGVs a key critical component of the future industrial landscape. Their development will continue to drive efficiency, safety, and productivity gains in many sectors, and thus signaling a new era of automation and operational excellence.
Choosing the right AGV solution
Selecting the appropriate Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) system is a critical decision for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency, safety, and scalability. The process involves a detailed analysis of several key factors and an understanding of how customization can meet specific requirements. Collaborating with vendors and technical experts is also crucial in navigating the vast number of options available. Here’s how to approach selecting the right AGV solution for your operations.
Factors to consider when selecting an AGV system
- Capacity: Evaluate the load capacity requirements of your operations. Consider the types of materials or products the AGV will transport, including their size, weight, and shape. Ensuring the AGV system can handle your current and future capacity needs is essential for long-term efficiency and productivity.
- Navigation: The layout and environmental conditions of your facility will significantly influence the choice of navigation technology. Evaluate the complexity of the paths, the presence of obstacles, and the level of variation in your operation area to determine whether magnetic spot, laser navigation, contour navigation, or another method is most appropriate.
- Safety: AGV systems must integrate into environments where humans and machines coexist. Look for AGV solutions that provide a comprehensive set of safety features, including emergency stops (E-stops), laser scanners, and warning signals. Compliance with safety standards such as ANSI/ITSDF B56.5 and EN ISO 3691-4 ensures that the AGV system adheres to industry best practices for safety.
The role of customization in meeting specific operational needs
Customization plays a crucial role in adapting AGV solutions to unique operational requirements. Whether it’s adapting the AGV’s load capacity, incorporating specific navigation technologies, or ensuring compatibility with existing warehouse management systems, customization ensures that the AGV system integrates smoothly into your operations. Get in touch with suppliers that offer customized solutions and have experience in dealing with specific challenges like yours.
How to work with suppliers and technical experts to find the best AGV solution
- Define your requirements: Clearly outline your operational needs, challenges, and objectives. Providing detailed information to suppliers helps them understand your context and recommend the most suitable AGV solution.
- Evaluate supplier expertise: Look for suppliers with extensive experience in your industry and with a portfolio of successful AGV implementations. Their expertise will be invaluable in navigating the complexities of AGV technology and integration.
- Seek collaborative engagement: The process of selecting an AGV system should be collaborative. Engage in discussions, ask for demonstrations, or reference visits, and consider pilot testing to evaluate the AGV’s performance in your specific environment.
- Consider after-sales support: The relationship with your AGV supplier should not end with the purchase. Consider the quality of after-sales support, including training, maintenance, and technical assistance, as this will be crucial for the long-term success of your AGV system.
Choosing the right AGV solution is a strategic process that affects the efficiency, safety, and adaptability of your business. By carefully considering the key factors, embracing customization, and working closely with experienced suppliers, companies can secure AGV systems that not only meet their current requirements but also allow for future growth and changes.
Conclusion
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) have become essential resources in the modern industrial landscape, revolutionizing how materials are transported in various sectors. These sophisticated systems not only streamline operations but also raise safety standards, increase productivity, and pave the way for the smart factories of the future. The critical role AGVs play in supporting and optimizing workflows, from manufacturing and warehousing to healthcare and beyond, is unquestionable. They are the silent workhorses that ensure operational continuity, adaptability, and efficiency.
As technology continues to develop, the capabilities of AGVs will expand even further, integrating more deeply with AI, machine learning, and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). This evolution will open the door to new levels of automation, precision, and intelligence in industrial operations, offering outstanding opportunities for growth and innovation.
The journey to fully embrace AGV technology can present challenges, including selecting the right system, ensuring complete integration, and navigating the complexities of modernization. Yet, the potential benefits are enormous. By choosing to invest in AGV technology, organizations not only future-proof their operations but also position themselves at the forefront of industrial innovation.
We encourage companies of all sizes and industries to get to know the benefits of AGV technology. In doing so, they can gain new efficiencies, improve safety, and achieve greater competitiveness in an ever-developing market. The future of successful operations is automated, and AGVs are a cornerstone of this new industrial era. Adopting AGV technology is not just an investment in automation but a commitment to the continuous improvement and long-term sustainability of your business.
Additional resources
For readers seeking more detailed information about Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), the following resources offer a wealth of knowledge, case studies, and whitepapers. These materials are designed to deepen your understanding of AGVs, their applications across various industries, and the latest developments in AGV technology.
- AGV case studies: Explore real-world applications of AGV systems and learn how they are changing operations in different sectors. Case Studies
- Brochures and materials: Access a collection of brochures and similar material that provide comprehensive information on AGV solutions, their features, and benefits. Brochures and Materials
- Whitepapers: Dive into in-depth analyses and discussions on AGV technology, including its implementation challenges, benefits, and future opportunities. Whitepapers
- AGV dictionary: A valuable resource for understanding the terminology, concepts, and technologies associated with AGVs. This dictionary covers everything from basic definitions to more complex technical descriptions. AGV Dictionary
- Videos: A variety of videos showcasing AGVs in action, demonstrating their capabilities, and highlighting their impact on efficiency and productivity. Videos
- AGV in manufacturing: Gain insights into how AGVs are revolutionizing manufacturing processes by enhancing efficiency, safety, and scalability. AGV in Manufacturing
- AGV battery technology: Learn about the different types of batteries used in AGVs and how they influence the performance and efficiency of these systems. AGV Battery
- The history of Automated Guided Vehicles: Trace the evolution of AGVs from their start to their current role as essential parts of modern industrial operations. The History of AGVs
These resources are intended to provide a solid foundation for understanding the critical role AGVs play in today’s industries and how they can be used to drive operational success. Whether you are new to the world of AGVs or looking to expand your existing knowledge, these materials offer valuable insights and perspectives.
AGV questions and answers:
What does AGV mean?
AGV stands for Automated Guided Vehicle. It is a mobile robot used for material handling in industrial environments. AGVs move autonomously using various navigation technologies such as lasers, magnets, or sensors. They are commonly used to transport loads safely and efficiently in factories, warehouses, and logistics centers.
How do the different navigation technologies affect the efficiency and flexibility of AGVs in various industrial environments?
Different navigation technologies offer varying levels of flexibility, accuracy, and infrastructure requirements. Magnetic and laser guidance systems provide high precision and reliability, ideal for structured environments but require physical modifications to the workspace. In contrast, natural feature navigation allows for more variability and adaptability, enabling AGVs to operate in changing environments without the need for dedicated paths. The choice of navigation technology has a major impact on the AGV’s ability to fulfil specific industrial needs, affecting efficiency and variability.
What are the main challenges and limitations of implementing AGVs in existing manufacturing or warehousing facilities, and how can they be overcome?
Challenges include integration with existing systems, the initial cost, and physical space requirements. Overcoming these challenges involves careful planning, selecting AGVs compatible with existing infrastructure, and potentially modifying layouts to accommodate AGV pathways. Using AGVs with advanced navigation systems that require minimal environmental changes can also reduce integration difficulties.
Given the developments in AGV safety technologies, how do AGVs contribute to creating safer work environments, and what standards regulate their safety?
AGVs contribute to safer work environments by reducing the need for human involvement in potentially hazardous operations, such as transporting heavy loads. Advanced safety features, like obstacle detection sensors and emergency stop buttons, further minimize the risk of accidents. Safety standards like ANSI/ITSDF B56.5 and EN ISO 3691-4 provide guidelines for AGV safety requirements, ensuring they operate safely alongside human workers.
How does the integration of AGVs with other smart technologies and systems, such as the Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), improve operational efficiency and decision-making?
Integration with WMS and other smart technologies enables real-time data exchange, allowing for more informed decision-making and efficient resource allocation. This synergy improves the coordination of material flow, optimizes inventory management, and improves the overall operational transparency, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
What are the key factors to consider when choosing between different types of AGVs for specific applications?
Key factors include the type and weight of materials to be handled, the required navigation precision, the operational environment’s complexity, and the integration capability with existing systems. Additionally, considering the specific operational goals, such as improving safety or increasing efficiency, can guide the selection process towards the most suitable AGV type.
In what ways are AGVs transforming the logistics and supply chain industry, especially in terms of automation, efficiency, and reliability?
AGVs automate material handling tasks, reducing manual labor, and minimizing errors. They provide consistent and reliable transportation of goods, enabling 24/7 operations and significantly improving supply chain efficiency. By seamlessly integrating with logistics systems, AGVs improve inventory accuracy, reduce turnaround times, and contribute to more agile and responsive supply chains.
How do the operational costs of AGVs compare to traditional material handling methods over the long term, and what factors contribute to their cost-effectiveness?
Although the initial investment in AGVs may be higher than traditional methods, the long-term operational costs are often lower due to reduced labor expenses, increased efficiency, and lower accident rates. Factors contributing to AGVs’ cost-effectiveness include their ability to operate continuously without fatigue, minimal maintenance requirements, and reduced product damage during transport.
What role do AGVs play in sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing and warehousing operations, particularly concerning energy consumption and carbon footprint reduction?
AGVs contribute to sustainability by optimizing material flow and reducing energy consumption through efficient routing and load handling. Electrically powered AGVs emit no direct emissions, helping to lower the carbon footprint of industrial operations. Additionally, the precision and efficiency of AGVs minimize waste, further supporting eco-friendly initiatives. Solving’s durable AGVs are built to last in tough industrial environments.
How can businesses prepare their infrastructure and workforce for the integration of AGVs, and what training or adjustments are necessary for smooth implementation?
Preparing for AGV integration involves evaluating and possibly modifying the physical layout to accommodate AGV operation, ensuring compatibility with existing systems, and addressing any connectivity requirements. Training for the workforce is crucial, focusing on system management, safety protocols, and emergency procedures to ensure a smooth transition and effective collaboration between humans and AGVs.
Looking towards the future, what new technologies or trends could further improve the capabilities and applications of AGVs in various industries?
Future improvements in AGV capabilities may include greater autonomy through AI and machine learning, improved interaction with humans and other machines through developments in IoT, and increased adaptability and decision-making capabilities. Trends such as Industry 4.0 and smart manufacturing will likely drive the development of AGVs that are more integrated, flexible, and capable of complex problem-solving, expanding their applications across a wider range of industries.